Introduction
As of June 2024, phishing remains as the most common form of cybercrime, with an estimated 3.4 billion spam emails sent every day (AAG-IT). Despite advancements in email security and detection controls, nothing is foolproof, meaning employees will inevitably be faced with phishing attacks that aim to exploit human vulnerabilities.
To help combat these threats, organizations can integrate phishing simulations into their security awareness programs and provide employees with hands-on experience in recognizing potential phishing attempts. When executed effectively, phishing simulations help employees build the skills and behavior needed to avoid, detect, and report suspicious emails—all while continually building a security-conscious culture across the organization.
Understanding Phishing
Phishing is a form of social engineering where attackers attempt to deceive people into either giving up sensitive information (intellectual property, credit card numbers, personal identification details, credentials), or installing malware, such as viruses, worms, or in worst cases, ransomware. To carry out phishing campaigns, attackers often impersonate legitimate entities and pair their deception with a number of common phishing techniques to get victims to click on a link, download a file, or enter information.
Types of Phishing
It’s also important to note that phishing can come in many different forms. The most common is Email Phishing, where attackers send malicious emails that appear to come from trusted sources, to persuade recipients into interacting with malicious links or attachments. Another common form is SMS Phishing (Smishing), which involves similar techniques and goals, but delivered through deceptive text messages. Similarly, Voice Phishing (Vishing) pairs social engineering tactics with impersonated phone calls to manipulate victims.
The Impact of Phishing Attacks
Recent statistics continue to show the prevalence and disastrous impact of phishing attacks. According to the Q2 2024 study conducted by the Anti-Phishing Working Group (APWG), the average amount requested in wire transfer Business Email Compromise attacks (where an attacker impersonates a known source and requests money) was $89,520, up 6.5% from Q1’s average of $84,059.
However, the impacts of successful phishing attacks go beyond just financial theft. Data breaches resulting from phishing can lead to expensive regulatory fines and other financial repercussions. In addition, the reputational damages that follow can hurt customer trust and confidence, potentially affecting long-term business relationships and market position. For example, in May 2021, Colonial Pipeline suffered a ransomware attack, likely triggered by a phishing email, which forced the company to halt operations for a week. The attack cost the company $4.4 million in ransom, with the overall damage, including non-delivery of oil worth approximately over $3 billion, making it one of the most expensive phishing-related incidents to date.
Security Awareness Training
Arguably, the most effective method we have to mitigate phishing success is training. Security awareness training is crucial because employees are seen as the first line of defense against many common threats that organizations face. Even the best technical security controls can be bypassed or rendered obsolete if employees aren’t properly trained to recognize and respond, and that’s what security awareness training aims to do – secure the human. Additionally, it helps cultivate a security-conscious culture across the organization. When employees understand the risks, they are more likely to follow best practices and report potential threats.
Typically, security awareness training programs are administered by the security or compliance team within an organization using vendors like KnowBe4, Beauceron Security, Proofpoint, Cofense, and many others. Each of these solutions can provide customizable training modules and reporting tools to measure employee engagement and awareness levels, sometimes in a gamified way. The training modules typically consist of interactive lessons or presentations that cover various topics such as recognizing suspicious emails, practicing good password hygiene, and understanding data protection policies. To reinforce learning, quizzes are often given to gauge comprehension and track progress.

From a compliance perspective, many industry regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS, mandate that organizations implement ongoing security awareness programs to make sure that employees are educated on data protection and privacy best practices. In turn, security awareness training tools often track and document training completion, making it easier for organizations to show evidence of their compliance efforts during audits.
Phishing Simulation Training
In order to effectively prepare employees to recognize and respond to real-world cyber threats, organizations will typically pair security awareness training programs with simulated phishing campaigns. Phishing simulations are just as their name suggests: They are simulated training exercises designed to test and educate employees about phishing attacks. In these simulations, an organization will send out fake, yet realistic phishing emails to employees to see how they respond. The goal is to gauge employees’ behavior and ability to recognize malicious emails that attempt to steal sensitive information, deliver malware, or compromise accounts or systems.
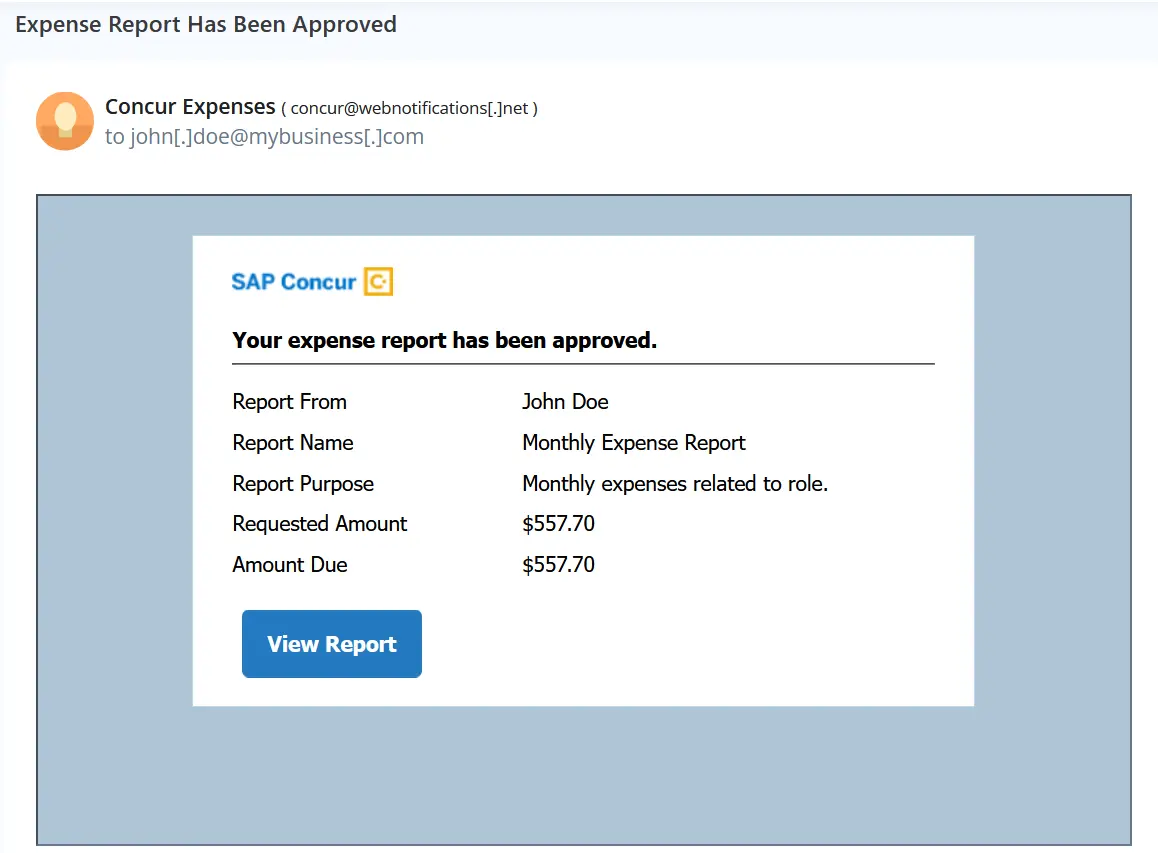
Below is an example of a simulated phishing email that imitates an expense report approval.
Types of Phishing Simulations
To properly prepare employees for the types of phishing emails they may encounter in their day-to-day activities, phishing simulations can be delivered in a number of formats, such as:
- URL Phishing – Phishing through simulated malicious links, sometimes directing users to a fake login page to capture their credentials.
- Attachment Phishing – Phishing through simulated malicious attachments and tracking if they’re downloaded, opened, or executed.
- QR Code Phishing – Phishing through QR codes that, when scanned, lead to simulated malicious sites or credential capture pages.
- SMS Phishing (Smishing) – Phishing through simulated malicious text messages.
- Voice Phishing (Vishing) – Phishing through simulated phone calls and attempts to extract information.
Typically, when integrating a phishing awareness training solution, organizations will deploy a report button in their email clients, allowing employees to easily flag suspicious emails for the security team to review. This feature is not only a best practice from an email security perspective, but it also encourages proactive behavior and helps employees practice reporting potential threats.

What Happens During Phishing Simulation Training
If an employee falls for the simulated attack (clicks on a link, scans a QR code, etc.), they might be asked to enter their credentials, which allows organizations to assess the scope of what would have been a legitimate compromise. In cases where employees fail to identify the phishing attempts, organizations may assign remedial training to reinforce the important takeaways and ensure a better understanding of email security security practices.
While awareness training modules are important for helping employees understand the risks, threats, and techniques associated with phishing attacks, the practical experience gained through phishing simulations is what really drives behavioral change. Simulations provide a tangible and interactive way for employees to apply what they have learned in a real-world context. When employees fall for a simulated attack, they receive immediate feedback, all within a safe environment with no actual impact. This reinforces their understanding of real-world phishing tactics and encourages them to adopt more cautious behavior in the future.
A practical approach like this is preferable because behavioral change often occurs through experience. By repeatedly engaging in phishing simulations, employees develop an unconscious sense for recognizing suspicious emails and requests.
Phishing Simulation Best Practices
Conduct Phishing Simulations at Regular Intervals
To be effective, phishing simulations should be conducted regularly. Quarterly or even monthly simulations can help ensure employees are continuously engaged and keep their skills sharp. It’s important to remember that real adversaries don’t typically work seasonally, and phishing campaigns can target organizations at any time.
Personalize the Content of Phishing Simulation Campaigns
Additionally, organizations will get the best results by tailoring their awareness campaigns to their own industry and reflecting simulations based on current threats and trends. For example, by varying the types of scenarios or tailoring simulations to specific tools and vendors the organization uses, this can prevent employees from simply recognizing the meta of the simulations rather than understanding the core lessons they aim to teach.
Treat Employees with Respect
Lastly, while phishing simulations are a valuable tool in the security awareness training arsenal, they should be conducted with consideration. Some companies inform their employees upfront that phishing simulations are going to occur, while others prefer to be more subtle with their approach.
Some organizations may choose to forgo specific phishing simulation templates that may be in bad faith (ie: emails regarding fake promotions, raises, or company gifts). However, others argue that anything is in scope because adversaries often employ tactics that exploit employees’ emotions and expectations. Either way, it’s important to encourage open participation, where employees feel comfortable reporting suspicious emails and learning from mistakes without fear of punishment.
Phishing Simulation Metrics
To assess the effectiveness of phishing simulations, organizations should track a number of metrics to paint the picture of the organization’s overall security awareness posture. Click rates are the most important metric to track. This metric indicates the percentage of employees who clicked on malicious links in simulated phishing emails. A high click rate typically means there is a lack of training or a breakdown of processes somewhere down the line. However, a decreasing click rate over time shows that the training is effective and organizational performance is improving.
Another similar metric is the credential capture rate, which shows how many employees entered their login information on a simulated phishing site. The detonation rate of malicious attachments can also be used to evaluate the effectiveness of your security awareness training.
Finally, ensure you are tracking the reporting rate, which identifies how many employees used the “report” button to flag phishing emails. A higher reporting rate indicates that employees are becoming more effective at identifying potential phishing emails, reflecting a positive behavioral shift.
Review the Data
Of course, it’s not enough just to track or even report on these metrics. To fuel the ongoing improvement feedback loop, organizations and phishing awareness administrators should regularly review the outcomes of their simulations to identify patterns and trends in employee responses. By doing so, organizations can make data-driven decisions on how to best target adjustments to training content or specific teams or employees, and focus on areas in which the organization is struggling.
For example, if a particular phishing tactic consistently results in high click rates across the organization, the phishing awareness program should enhance training to specifically address that tactic. Additionally, involving employees in discussions or post-incident interviews about their experiences during simulations and failures can provide additional feedback on what areas of training could be improved.
Conclusion
When building out a phishing awareness training program, it’s important to address each organization’s unique human vulnerabilities and industry-specific threats. To effectively secure the human and foster more security-centric behavior, theoretical training should be combined with regular, practical simulations that reflect real-world phishing scenarios. Ultimately, a proactive approach to phishing awareness not only strengthens the organization’s cybersecurity posture but also builds up a security-conscious culture across the organization that extends beyond the first line of defense.

About the Author: Andrew Prince
Andrew is a seasoned and passionate security professional who brings a wealth of experience in areas such as security operations, incident response, threat hunting, vulnerability management, and cloud infrastructure security. With a professional background in development and system administration, Andrew offers a well-rounded perspective on his security strategy. Andrew also navigates both offensive and defensive operations to provide a holistic approach to keeping people, processes, and technology secure. He is also active in developing various Capture the Flag challenges, creating security training, and sharing knowledge through content creation. Andrew created the Security Operations (SOC) 101 course in TCM Security Academy and the Practical Junior Security Analyst certification.
Social Media Links:
About TCM Security
TCM Security is a veteran-owned, cybersecurity services and education company founded in Charlotte, NC. Our services division has the mission of protecting people, sensitive data, and systems. With decades of combined experience, thousands of hours of practice, and core values from our time in service, we use our skill set to secure your environment. The TCM Security Academy is an educational platform dedicated to providing affordable, top-notch cybersecurity training to our individual students and corporate clients including both self-paced and instructor-led online courses as well as custom training solutions. We also provide several vendor-agnostic, practical hands-on certification exams to ensure proven job-ready skills to prospective employers.
Pentest Services: https://tcmdev.tcmsecurity.com/our-services/
Follow Us: Blog | LinkedIn | YouTube | Twitter | Facebook | Instagram
Contact Us: sales@tcm-sec.com
See How We Can Secure Your Assets
Let’s talk about how TCM Security can solve your cybersecurity needs. Give us a call, send us an e-mail, or fill out the contact form below to get started.

